VOMER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Interactive 3D Version Available
Explore this anatomy in full 360° rotation with our interactive 3D viewer
View in 3D →VOMER AR ATLAS
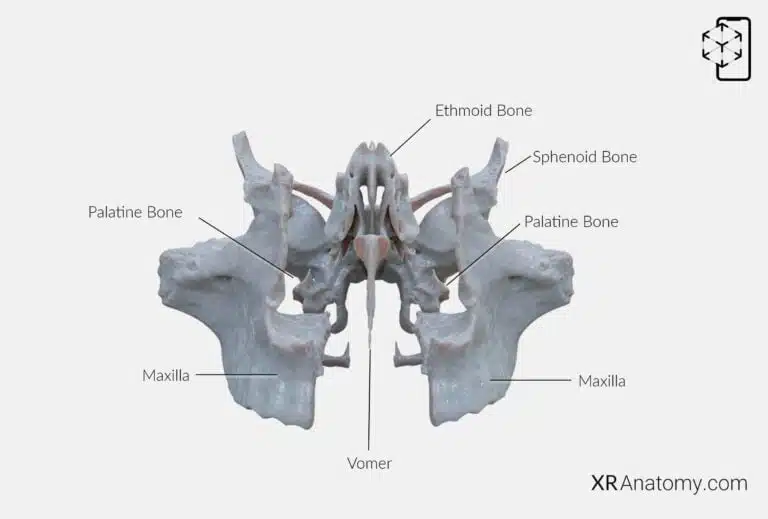
AR Figure 70 – Vomer: Disarticulated view, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The vomer is a slender, unpaired bone situated in the midsagittal plane of the skull, forming the inferior portion of the nasal septum. It plays a crucial role in separating the left and right nasal passages, contributing to the nasal cavity's structure and function. The vomer several bones, including: The sphenoid bone, The two maxillae, The palatine bones, The ethmoid bone.
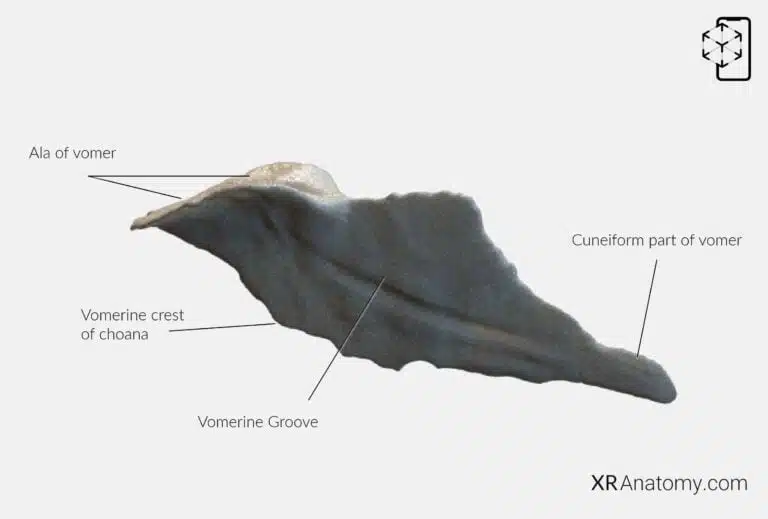
AR Figure 71 – Vomer, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
Its superior border features two wing-like projections called the alae of the vomer, which extend laterally on either side. These alae the sphenoid bone via the vaginal processes of the medial pterygoid plates and with the palatine bones through the sphenoidal processes, anchoring the vomer securely within the skull. Along the surface of the vomer runs the vomerine groove, an oblique indentation that accommodates blood vessels and nerves supplying the nasal septum. The posterior border of the vomer forms the vomerine crest of choana, contributing to the structure of the choanae—the openings between the nasal cavity and the nasopharynx. At the anterior aspect, the cuneiform part of the vomer presents a wedge-shaped portion that connects with the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and the septal cartilage, completing the nasal septum. This configuration ensures proper separation of the nasal passages, which is essential for efficient airflow and olfaction.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Sampson HW, Montgomery JL, Henryson GL. Atlas of the human skull. College Station: Texas A & M University Press; 2007.
4. Saylam C, Özer MA, Ozek C, Gurler T. Anatomical Variations of the Frontal and Supraorbital Transcranial Passages. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2003;14(1):10–2.
5. Hosemann W, Gross R, Goede U, Kuehnel T. Clinical anatomy of the nasal process of the frontal bone (spina nasalis interna). Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery. 2001;125(1):60–5.
6. Steele DG, Bramblett CA. The anatomy and biology of human skeleton. Texas A&M University Press; 1988.
7. Tersigni-Tarrant MTA, Shirley NR. Human osteology. Vol. 4, Forensic Anthropology: An Introduction. 2012. 33–68 p.
8. Monjas-Cánovas I, García-Garrigós E, Arenas-Jiménez JJ, Abarca-Olivas J, Sánchez-Del Campo F, Gras-Albert JR. Radiological Anatomy of the Ethmoidal Arteries: CT Cadaver Study. Acta Otorrinolaringologica (English Edition). 2011;62(5):367–74.
9. Pereira G, Lopes P, Santos A, Krebs. Morphometric aspects of the jugular foramen in dry skulls of adult individuals in Southern Brazil. Vol. 27, J. Morphol. Sci. 2010.
12. Kunc V, Fabik J, Kubickova B, Kachlik D. Vermian fossa or median occipital fossa revisited: Prevalence and clinical anatomy. Annals of Anatomy. 2020 May 1;229:151458.
14. Standring S. The skull. In: Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 2021st ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2021. p. 558–73.
15. Rhoton AL. Chapter 1 Overview of Temporal Bone. Neurosurgery. 2007;
17. Tóth M, Moser G, Patonay L, Oláh I. Development of the anterior chordal canal. Annals of Anatomy. 2006;
18. Carpenter G, Knipe H. Tympanic part of temporal bone. Radiopaedia.org. 2014 Mar 23;
19. Eckerdal O. The petrotympanic fissure: A link connecting the tympanic cavity and the temporomandibular joint. Cranio – Journal of Craniomandibular Practice. 1991;9(1):15–22.
21. Singh R, Kishore Gupta N, Kumar R. Morphometry and Morphology of Foramen Petrosum in Indian Population. Basic Sciences of Medicine. 2020;2020(1):8–9.
23. Piagkou M, Xanthos T, Anagnostopoulou S, Demesticha T, Kotsiomitis E, Piagkos G, et al. Anatomical variation and morphology in the position of the palatine foramina in adult human skulls from Greece. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. 2012 Oct 1;40(7):e206–10.